In our first exercise we will do some hands on with Python's in built methods.
Store your own version of the message "Hello World" in a variable, and print it.
Store your own version of the message "Hello World" in a variable, and print it.
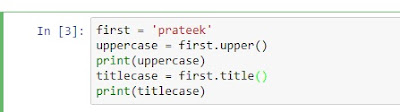
Store your first name, in lowercase, in a variable.Using that one variable, print your name in lowercase, Titlecase, and UPPERCASE.
Choose a person you look up to. Store their first and last names in separate variables.
Use concatenation to make a sentence about this person, and store that sentence in a variable.-
Print the sentence.
Store your first name in a variable, but include at least two kinds of whitespace on each side of your name.
Print your name as it is stored.
Print your name with whitespace stripped from the left side, then from the right side, then from both sides.
So keep practicing by your own with above examples in your notebook and comment if you face any issue.



squaldasusoFort Collins Shelly Mann https://wakelet.com/wake/dy2po223ilpmqxzapvo-y
ReplyDeleteascenrala
charpiYgastmi Peter Ramirez WinZip
ReplyDeleteEset NOD 32
WonderShare Recoverit
ektravgitu
Data Science Certification in Pune
ReplyDeleteData Science Training Institute in Pune
Data Science Certification in Pune
Data Science Training Institute in Pune
Data Science Certification in Pune
Data Science Training Institute in Pune
Data Science Certification in Pune
Data Science Training Institute in Pune